Part 01: Classification of Fruits.
A) Botanical Classification:


B) Climatic Adaptability:
A) Tropical Fruits:
Tropical fruits are a diverse group of fruits that thrive in warm, tropical climates characterized by high temperatures and abundant rainfall. These fruits are typically native to tropical regions around the equator and are known for their vibrant flavors, unique textures, and nutritional benefits.
Examples:
- Mango
- Banana
- Papaya
- Pineapple
- Guava
- Sapota
- Custard Apple
- Jackfruit
- Carambola
- Persimon
- Coconut
- Cashew
B) Temperate Fruits:
Temperate fruits refer to fruits that are cultivated in temperate climates, which are characterized by distinct seasons including moderate temperatures, defined spring and autumn periods, and typically cold winters.
Examples:
- Apple
- Pear
- Plum
- Walnut
- Peach
- Apricot
- Almond
- Cherry
- Strawberry
- Pecanut
C) Arid and Semi Arid Fruits:
- Ber
- Aonla
- Date Palm
- Bael
- Phalsa
- Jamun
- Karonda
D) Subtropical Fruits:
Subtropical fruits are a category of fruits that thrive in regions with subtropical climates, characterized by mild to warm temperatures year-round, with mild winters and hot summers.
Examples:
- Mandarin
- Sweet Orange
- Fig
- Litchi
- Grape
- Annona
- Pomegranate
- Avocado
- Loquat
- Mango Stem
- Rambutan
C) Fruit morphology:
A) Simple Fruits:
- Berry: Banana, Papaya, Grapes, Sapota, Arecanut and Avocado.
- Modified Berry:
a) Balausta: Pomegranate.
b) Amphisarca: Wood Apple, Bael.
c) Pepo: Watermelon.
d) Pome: Apple, Pear, Quince, Loquat.
e) Drupe (Stone): Mango, Peach, Plum, Ber, Coconut, Cherry, Cocoa, Coffee.
f) Hesperidium: Citrus.
g) Nut: Cashew, Litchi, Chesnut, Walnut, Pecanut, Rambutan.
h) Capsule: Aonla, Carambola.
B) Aggregate Fruits:
a) Etaerio of Barries: Custard Apple, Raspberry.
b) Etaerio of Druplets: Blackberry.
c) Etaerio of Achenes: Strawberry.
d) Etaerio of Follicles: Caiharanthus.
C) Multiple Fruits:
a) Syconus: Fig.
b) Sorosis: Jackfruit, Pineapple, Mulberry, Breadfruit.
D) Rate Of Respiration:
A) Climacteric Fruits:
“Sharp rise in Respiration after harvesting.”
Examples:
- Mango
- Banana
- Sapota
- Guava
- Papaya
- Apple
- Fig
- Peach
- Pear
- Plum
- Annona
- Jackfruit
- Avocado.
B) Non Climacteric Fruits:
“Steady respiration at the time of harvesting.”
Examples:
- Citrus
- Grapes
- Pineapple
- Pomegranate
- Litchi
- Ber
- Jamun
- Cashew
- Cherry
- Strawberry
- Aonla
- Loquat
- Phalsa.
Note: *Climacteric Fruits produce much larger amount of ethylene than non Climacteric Fruits.
*Highest ethylene production a) Apple-25 to 2500 µL/L.
b) Passion Fruit- 466 to 530 µL/L.
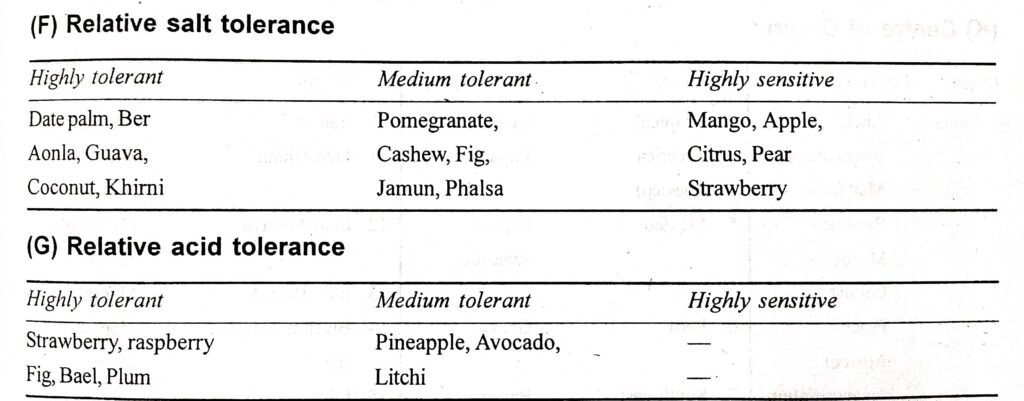
(E) Photoperiodic Responses:
1) Long Day Plant:
- Passion Fruit
- Banana
- Apple
- Date Palm
- Ber
- Aonla
- Guava
- Coconut
- Khirni
2) Short Day Plant:
- Strawberry
- Pineapple
- Coffee
- Pomegranate
- Cashew
- Fig
- Jamun
- Phalsa
3) Day Neutral Plant:
- Papaya
- Guava
- Mango
- Apple
- Citrus
- Pear